Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: together for better treatment
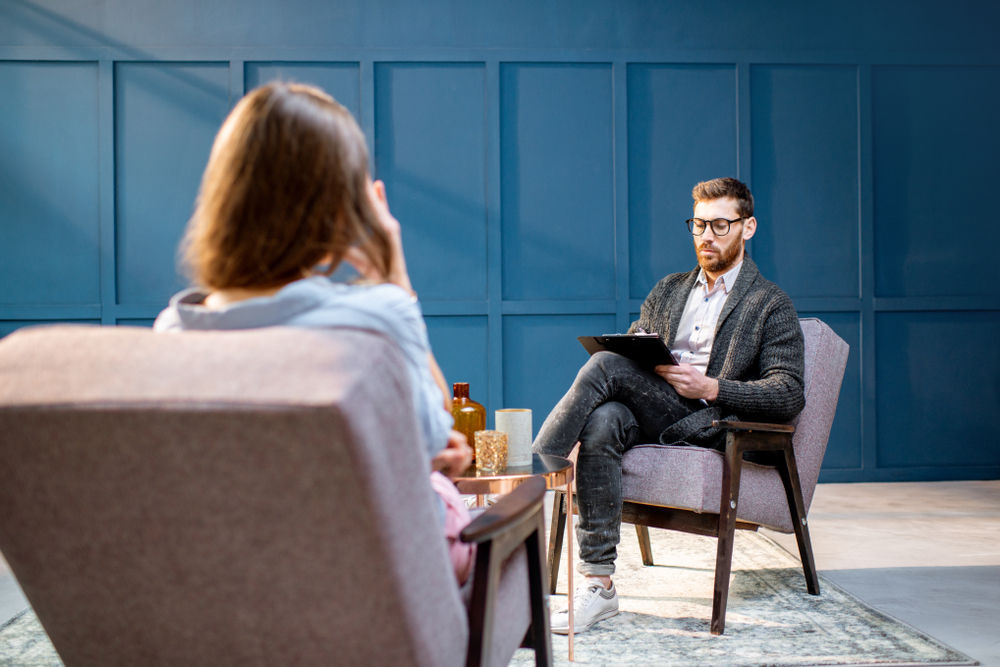
Psychologist vs psychiatrist has been a question on the minds of a plethora of people who are seeking professional help. In the society that we live in today, we sometimes do not have time for ourselves. In between the appointments, classes, work, supermarkets, mortgages and an occasional workout we forget to take care of our mind. When people think about health, they usually look into the physical aspects of what we consider healthy. Somebody who follows a healthy diet that consists of all the needed macro and micro-nutrients. Somebody who takes the time to exercise a few times a week. A person that plays a sport. These are the people that inspire us and these are the people we aspire to be. In chasing the goal of a perfect physical health, we often forget about our mental health.
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: Education

Psychologists
If your goal is to pursue a career in psychology you will first need an undergraduate degree in psychology. After that, and, depending on a country, psychologists will be required to go to graduate school. In graduate school, they will obtain a title of a Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) or a Doctor of Psychology (PsyD).
Students need to be careful with the distinction of the two. Some countries consider a Ph.D. degree to be a solely research oriented doctoral title that does not allow a person to practice with people. In many countries throughout the Ph.D. degree, the students are required to develop and design a scientific study. In the end of their doctoral degree, the students will write a dissertation and present it to specifically assigned judges. They might then go on to pursue a postdoctoral fellowship and continue their work in research. PsyD is considered to be a clinical degree. It does not include a research aspect and is solely focused on producing practitioners in the field of mental health. Many times before a Ph.D. or a PsyD degree can be obtained, students are required to undergo a one or two-year Master of Science degree.
Throughout the course of their clinical training future psychologists will have constant supervision. They will have practicums with different age-groups and different mental health problem populations.
Psychologists can differ from one another in regards with different treatment approaches. The majority fall between the two categories, one being the psychodynamic approach and the other – cognitive-behavioral therapy.
In many countries, only those who complete all the required conditions and certified themselves will then be able to use the protected title of a “psychologist”.
Psychiatrists
Psychiatrists need to get proper medical training. They will have the same medical education as every other medical doctor you might see if you go to a hospital. Instead of a Ph.D. or a PsyD degree, psychiatrists will hold a Doctor of Medicine degree (MD). Depending on the country medical schools have different requirements.
In the United States, a student needs to complete an undergraduate degree and then apply for medical school where they will spend 4 years. In the UK, for example, medical school lasts for 5 years and students apply straight after finishing secondary education. After the completion of medical school students have to undergo different residency or foundation programs in order to be considered fully specialized and trained psychiatrists. In the US the training lasts for 4 years and that’s where the students specialize in Psychiatry. The UK students study for 2 additional Foundation years where they practice in hospitals before they can specialize. After that, they take 4 years and have to pass two exams in their specialization.
Psychiatrists train in diagnosis and treatment for various mental disorders like schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. They also get training in a different psychotherapeutic treatment approach like cognitive-behavioral therapy. Many psychiatrists then further specialize in the fields of neuropsychiatry, geriatrics, psychopharmacology, and others. Compared with psychologists, psychiatrists treat people who have more severe mental problems. These mental disorders usually required prescribed medicine.
That is where one of the main distinctions between a psychologist and a psychiatrist comes in. Being fully trained medical doctors psychiatrists are allowed to prescribe drugs to their patients, while psychologists cannot do so. Psychologists have to refer their patients for medication.
Job Outlook & Salary
Bureau says that both, psychologists and psychiatrists have a similar job outlook. The salary is different for both of the professions, however, with major differences between countries as well. Psychiatrists, being qualified medical doctors, earn significantly more money than psychologists do. Their average salary rounds up to about $160,000 in the U.S. with psychologists almost reaching the $70,000 mark in the United States in 2010.
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: similarities
The similarity is quite obvious. Both of the professions deal with people who have mental health problems. They will both will try and help you with these problems by talking and offering therapy. Both of the professions will attempt to arm you with the tools to solve your issues. Apart from treating patients, both of the professionals keep up with the recent and up-to-date research and sometimes, both of them can participate in the ongoing investigations. These investigations can deal with a variety of topics ranging from psychophysical studies to brain studies with the use of neuroimaging methods.
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: differences
The professions have different regulations, distinct certificates, and licensing procedures. On top of that, different countries have different ways of categorizing these two. Countries tend to protect certain profession titles. Education professions and doctors usually fall under the category of protected titles. Psychologists and psychiatrists do too in the majority of nations. This happens due to the fact that both of the professions have a high contact with the society. And if one were to think about the population both psychologists and psychiatrists have to deal with on a daily basis, they start to understand why the protected titles are necessary. This all sounds confusing and, in reality, it is.
Both professions treat in a different way as well. Psychologists can treat in a variety of different ways depending on their approaches: psychodynamic, cognitive-behavioral, humanistic.
Psychiatrists, being medical doctors, rely more on pharmacological approaches in combination with the most common therapy for given disorders.
Apart from those who are suffering from disorders, there are many who would like to pursue a career in mental studies. The question of psychologist vs psychiatrist comes up again. Both of the professions require a different amount of study, different perspectives, and opportunities. Apart from just clear cut clinicians, there are many sub-fields in both specialties. The psychologist vs psychiatrist problem then becomes even more confusing. Students should be able to learn the difference between the two and understand the different ways both professions can take them.
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: mental disorders
We don’t often focus on the things that we truly enjoy. Maybe we focus on things that others like and with that, we undermine our own wants. Everybody’s needs are different and not a lot of people know or have the ability to satisfy their own needs. This can lead to many various conditions that undermine our mental health. People fall into spirals of depression, develop different types of anxiety and phobias.
This is just the iceberg of some mental disorders that can be influenced by the environment. We also cannot forget the genetic component. Both depression and anxiety have a link to genetics. Apart from these two disorders, we have a variety of others. Learning and attention disabilities are appearing more and more in various countries. Developmental and personality disorders are becoming more often. Some countries diagnose their population a bit too much, others do not understand the notion of a mental disorder.
The psychologist vs psychiatrist question also comes up due to the fact that psychologists and psychiatrists are able to view mental disorders in a different way. When people find themselves in trouble they should be able to ask for professional help and they should be able to know who to ask for help. The psychologist vs psychiatrist dilemma that many people face should not be one.
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: Major Depression
Different countries will have different regulations for the diagnosis of various mental disorders. In the US, both of the professionals will look at the last edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual to diagnose a patient and treat him or her with depression. The diagnosis will be quite similar to the Major Depressive Disorder with symptoms ranging from loss of interest or anhedonia, depressed mood, feeling sad, guilt and worthlessness and many other symptoms. A professional needs to be able to check off 5 from the list in order to be able to diagnose a patient with a Major Depressive Disorder.
Psychiatrists: Major Depression
A psychiatrist will pursue a series of activities and interventions. The doctors will provide these therapeutic techniques throughout the process of treatment. Before the start of treatment, they will establish a therapeutic relationship with the patient. The patient should be aware of all of the treatment procedures and the psychiatrist will take into account the preferences of the patients.
Psychiatrists will then compose a complete psychiatric history of the patient. They will look for manic symptoms in order to conclude that it is indeed major depression and not bipolar disorder. The doctors will look at any treatments that the patient has undergone or is undergoing at the moment. This step will especially include the history of all of the side effects, if any, to prescribed medication, the assigned dosages and how long the patients were taking the medicine.
Being doctors, psychiatrists will compose the general medical history and overlook any other medications that the patient might be taking. Importantly, they will check for substance use history and whether the patient has undergone treatment for those if present. Psychiatrists will then compose an individual history of the patient including the major events that happened to the patient, social, work related history, and family histories.
Psychiatrists: Major Depression treatment
These clinicians will also assess the patients based on suicide risk and hospitalize them, if necessary. Then, they will consider a treatment setting for the patient that is the most appropriate and the least binding, if conditions allow. Psychiatrists will then attempt to maximize the quality of life of the patient which includes personal hygiene, interpersonal and work relationships etc. They will then establish a connection with all of the other clinicians that are overseeing the patient.
When choosing the initial treatment, psychiatrist’s goal is to reduce the symptoms and promote remission of the episode. Doctors need to look at how severe the symptoms are and other factors that might contribute to patients’ depression (biological, environmental, social). They need to take into account patient’s preferences. (1) Psychiatrists need to consider which treatment methods would be the best for a particular patient, both providing pharmacotherapy in the form of anti-depressants (in the case of psychotic features, antipsychotic medication) and combining with psychotherapy. In certain cases, psychiatrists may consider electroconvulsive therapy for, especially severe cases.
Psychologists: Major Depression
Psychologists will pursue a series of activities and interventions for the patients as well and establish a therapeutic relationship. They will also keep track of all of the psychiatric, personal and social history of the patient.
Psychologists will mainly use psychotherapy in order to treat depression, depending on their approach. It is especially helpful when the depression is in the mild or moderate form. They will help the patients understand the life events that could have led to depression itself. They will help the patients to accept these life events and look towards the future with practical goals. Psychologists will focus on cognitive distortions of the patient and maladaptive thoughts and try to decrease the feelings of helplessness and hopelessness in the patient. They will help the patients learn how to deal with the milestones in their life and the symptoms in order to prevent depression in the future.
For the most part, psychologists use two different types of therapy:
- Interpersonal Therapy (IPT): this is where patients learn how to deal with their social relationships and to communicate their emotions in a better and more adaptive way. IPT focuses on learning new social skills and creating a support circle around the patient.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): psychologists help patients realize the maladaptive thought and try to teach them to realize when the thoughts occur. They also try to teach the patients to change the thoughts and behaviors that contribute to depression and focus on social skills.
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: Anxiety
There are many different types of anxiety. Both psychologists and psychiatrists are able to treat anxiety and the phobias that might be associated with it. A psychologist might be able to treat various phobias with the help of exposure therapy and behavioral techniques and help ease some behavior patterns that appear in anxiety. Psychologists can offer to counsel and achieve those behavioral changes. They can help with abuse and trauma. A psychiatrist will be able to diagnose you right away and will deal with more severe types of anxiety. Since a psychiatrist is a medical doctor he or she will be able to prescribe medication along with providing psychotherapy.
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: similarities in treating mental disorders treatment
Both professionals can treat psychiatric disorders in a similar fashion. For example, in the case of major depression, it is quite common to combine psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy in order to achieve maximum goals. Both psychiatrists and psychologists recognize that and implement it into their treatment strategies.
Psychologist vs Psychiatrist: differences in treating mental disorders treatment
In some cases, however, psychiatrists and psychologists differ in their approach to treating certain psychiatric problems. A great example would be bipolar disorder. The goal of a psychiatrist is usually to help the patient autonomously manage medication due to the fact that bipolar disorder requires medication that lasts for quite a while, if not for life. This is psychiatrist’s primary focus when it comes to patients diagnosed with bipolar disorder.
Psychologists, on the other hand, recognize the fact that patients with bipolar disorder need pharmacotherapy, but they focus more on psychotherapy. They can use cognitive-behavioral therapy for both the depression and the manic phases of the disorder, helping with thought distortions and maladaptive behaviors that happen as a result of the disorder.
Psychologist vs. Psychiatrist: Who should you see?
Patients will usually see a primary physician first. The primary physician will refer these patients to a licensed and certified clinical psychologist. This psychologist will start therapy with the individual and work on making the patient look at their own thoughts and behaviors.
For disorders that are more serious in nature (e.g. schizophrenia, bipolar disorder) should see a psychiatrist for a proper medication treatment plan. For mild to moderate depression, anxiety, stress it is better to see a psychologist who can then refer you to a psychiatrist, if needed, for pharmacotherapy and further treatment.
A psychiatrist can come in as a referral from a psychologist for a prescription of medicine. After that, the two professionals work together in order to achieve the best and proper individualized treatment for the patient in hand.
At times, both of the professionals can view various mental problems from different perspectives.
The goal for both professions is to provide the best possible treatment. We cannot say that one of the professions is better than the other one because both of them work for the good of the people. Often times they work together in a collaboration to help their patients.
Bibliography
American Psychiatric Association. Treating Major Depressive Disorder: A Quick Reference Guide. Practice. 2010;(October):1–28.