Digits Mathematical Puzzle – A Favorite CogniFit Game
CogniFit works hard to continue providing our users with the highest quality games and activities with new releases every week. One of our top played brain games is a fun and challenging mathematical game called Digits.
ABOUT DIGITS MATHEMATICAL PUZZLE
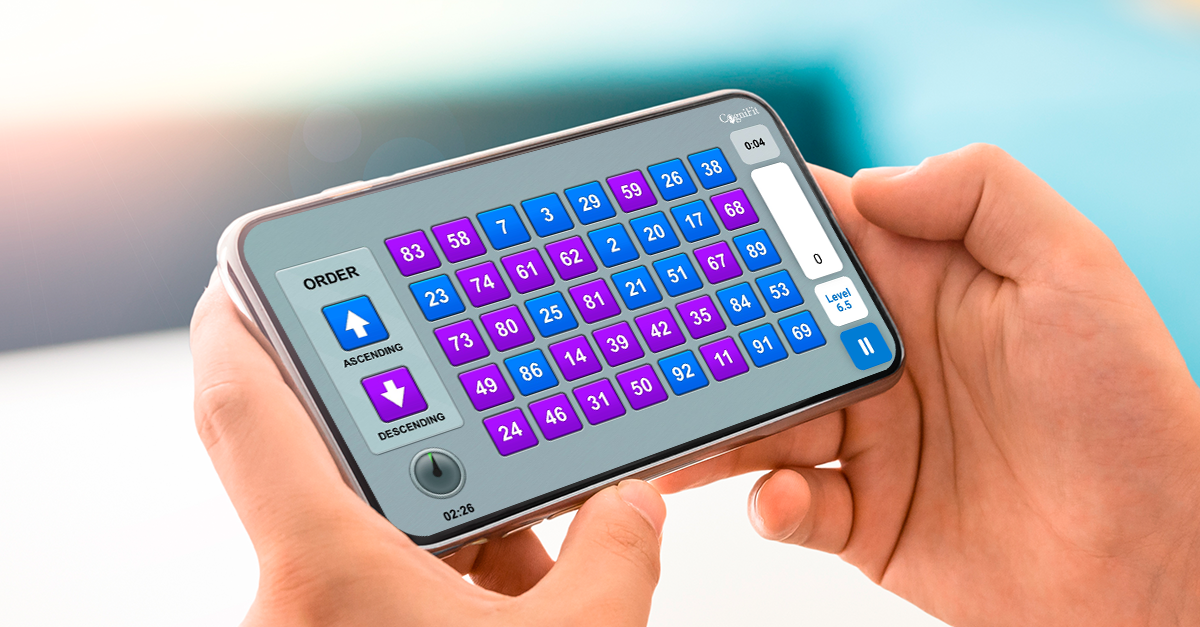
Digits is a mathematical puzzle game that tests the user’s ability to quickly organize numbers according to the indicated rules.
While the game starts out simple enough users should keep their focus because the game can quickly present a challenge for even the sharpest minds. As the game progresses, not only does the quantity of numbers increase, but also the complexity of the rules.
HOW TO PLAY DIGITS MATHEMATICAL PUZZLE
The objective of Digits is to organize the various numbers in an ascending and/or descending order based on the rules indicated at each moment. As the level increases, the number of digits to order will also increase. Users need to stay focused and order the numbers as quickly as possible, trying to avoid mistakes that can cause them to lose points.
THE SCIENCE BEHIND THE GAME
Digits has been developed with the key cognitive abilities in mind: Processing speed, Working Memory, & Visual Scanning.
While playing Digits, users are stimulating specific neural activation patterns related to these cognitive abilities. Repeating and training these patterns consistently can help create new synapses. And, in turn, help neural circuits reorganize and regain weakened or damaged cognitive functions.
Let’s take a look at these core cognitive abilities – how they help us with tasks in our everyday lives, and what makes them so important:
Processing Speed

Processing speed is one of the main cognitive abilities we rely on every day. It is a core aspect of learning, academic performance, intellectual development, reasoning, and experience.
Processing speed is a cognitive ability defined as the time it takes a person to process a situation or stimulus and develop a response. It is related to the speed at which a person can understand and react to the information they receive. This can be visual (letters and numbers), auditory (language), or movement.
Poor processing speed does not mean that a person is unintelligent. Instead, it means that some tasks may require more time to perform. This can include things like reading, doing math, taking notes, or holding conversations. It may also interfere with executive functions. Because a person with a slow processing speed will have a harder time planning, setting goals, making decisions, starting tasks, or paying attention.
Working Memory

Working memory (or operative memory) is the set of processes that allow us to store and manipulate temporary information and carry-out complex cognitive tasks. This includes things like language comprehension, reading, learning, or reasoning. Working memory is a type of short-term memory.
Working memory, according to Baddley and Hitch, is made up of several systems…
- The Central Executive System: It works like an attention supervision system that decides what we pay attention to and how to organize a sequence of operations that we will need in order to do action.
- The Phonological Loop: This allows us to manage and retain spoken and written material in our memory.
- The Visual-spatial Agenda: We can manage and retain visual information.
- The Episodic Buffer: Integrates information from the phonological loop, visuospatial sketchpad, long-term memory, and the perceptive entrance into a coherent sequence.
Without working memory, we wouldn’t be able to…
- Integrate two or more things that took place close together. For example, remembering and responding to the information that was said during a conversation.
- Associate a new concept with previous ideas. It allows us to learn
- Retain information while we pay attention to something else. E.g. following a recipe while we talk on the phone.
We use our working or operative memory on a daily basis for a number of tasks. For students it lets them take notes at school. They need to remember what the teacher said so that they can write it down in their own words. For adults, it’s when we do mental math in the supermarket to see if we have enough money to pay.
Visual Scanning

Visual scanning is the ability to efficiently, quickly, and actively look for information relevant to your environment. It is what makes it possible to find what you’re looking for using just your vision. Visual scanning is an important skill for daily life and makes it possible to efficiently carry out a number of different tasks.
Visual scanning is a function of visual perception that is aimed at detecting and recognizing visual stimuli. When you want to find something in your around you, your brain will automatically go through a series of interrelated processes:
- Selective and Focused Attention: You need to be aware and focused on a stimulus in order to find it. Selective attention, however, is the ability to pay attention to a single stimulus when there are distracting stimuli present.
- Visual Perception: Makes it possible to distinguish, identify, and interpret shapes, colors, and lights. This is when you make sense of the information that you receive from your eyes.
- Recognition: Comparing the visual information you receive to determine whether or not you have prior experience with this information.
- Visual Scanning: Looking through all or part of your field of view in order to compare what you’re seeing to what you’re looking for. You will stop looking as soon as you recognize the information that you’re looking for.
If any of these processes are altered, it would be impossible to locate a target object. Either because you can’t find it (poor attention), because you can’t distinguish the object from its surroundings (poor perception), because you don’t recognize the stimulus (poor recognition), or because you don’t properly scan the area (poor visual scanning).

There are a number of jobs that require visual scanning.
Police officers or members of the military have to be able to quickly and precisely detect objects that may be dangerous. Store employees have to use visual scanning to keep an eye out for products that may be misplaced or clients that need help. Almost any job has some level of a visual component that requires good visual scanning.
Students are constantly using visual scanning at school, whether it’s to pay attention to the board, read a book, or understand a presentation.
Driving requires you to constantly be on the lookout for other cars, accidents, potential hazards, traffic signs, pedestrians, and a number of other objects or situations. Poor visual scanning may inhibit your ability to successfully scan the environment for potential problems, decreasing your driving ability.
Visual scanning is an essential part of playing sports. Most sports require you to easily and quickly scan the space for relevant stimuli, which may be teammates, rivals, a ball, a goal, or any other vital component of the game. If you are playing football and want to pass the ball to a teammate, you have to visually scan the field to find him or her and then pass the ball to them.
DIGITS MATHEMATICAL PUZZLE – CONCLUSION
One of the fundamental parts of mathematics is the numerical value. If one figure is greater than, equal to, or less than another. This is something that we learn in childhood. However, it can be challenging to apply it in the real world when under pressure.
CogniFit’s newest game Digits presents an engaging and fun way to train cognitive skills. With it, we can keep a sharp mind and boost our abilities related to numerical value.