Happy Hopper: A Challenging Game for Training Response Time
Happy Hopper is our newest cognitive stimulation game is fun, exciting, and a great way to get some sweet revenge on those pesky flies that kept buzzing around your most recent picnic!
We are proud to announce Happy Hopper, an entertaining yet challenging cognitive stimulation game! It’s sure to have you jumping with joy while you train some of your most important cognitive abilities!
ABOUT HAPPY HOPPER
In Happy Hopper, you have to help our froggy friend reach the cloud of flies by jumping on the stones. But you’ll have to avoid all the obstacles along the way.
This game has been designed to stimulate Response Time by helping the frog jump on top of fast-moving stones. Like all of CogniFit’s games, Happy Hopper adapts the difficulty level according to the level. This means it’s suitable for everyone from 7 years old and up. Happy Hopper is perfect for those who want to stimulate their mind and help strengthen cognitive skills.
HOW TO PLAY HAPPY HOPPER
The concept of the game is fairly straightforward. The player must jump on top of moving platforms in order to reach a swarm of flies at the top. Different kinds of stones, stumps, or grass-covered platforms will fly by your frog. And, you have to decide what to do with them as fast as possible.
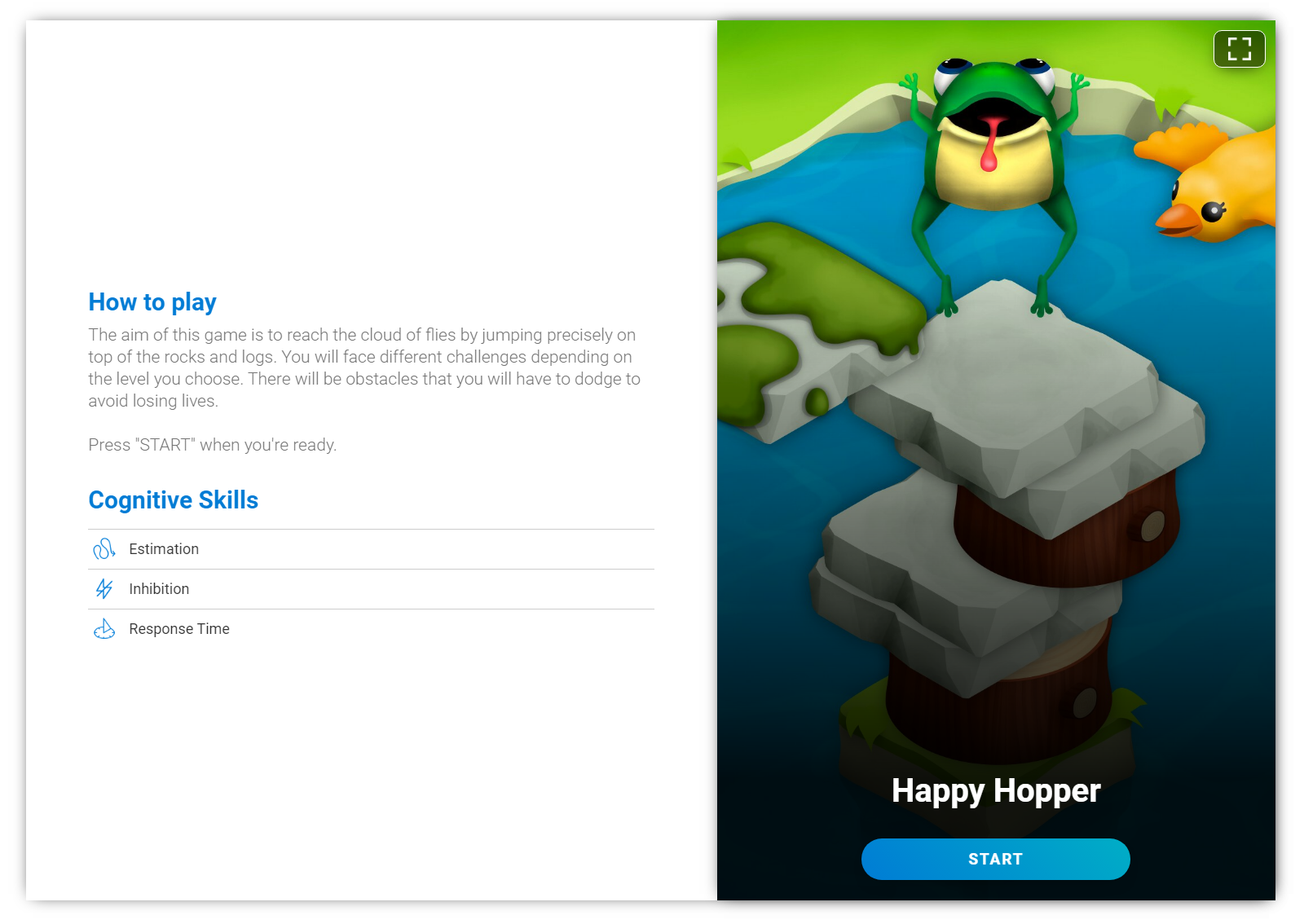
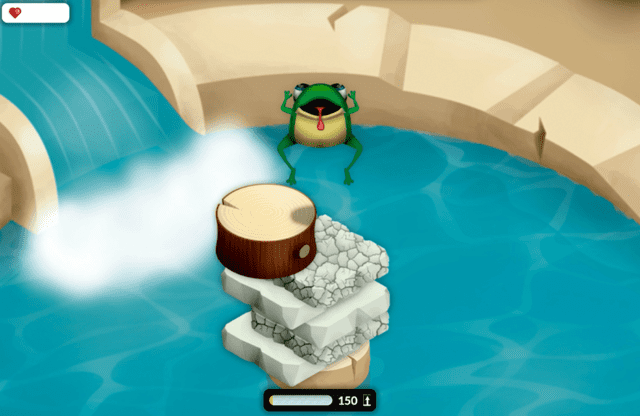
However, things aren’t always as easy as they seem. The platforms move quickly. Some even have cracks in them and will break if the frog lands on them too many times.
In addition, there are other obstacles that might block your progress.
- Diving Birds: These birds fly at an angle and try to hit the frog. Even though they fly quite slowly, they can still be dangerous.
- Flapping Bats: These pests act same way as the birds, but they are much faster and more difficult to avoid.
- Moss-Covered Platforms: Not all platforms are safe for the frog. Sometimes you will see rocks and logs covered in green moss. If the frog lands on one of these, they will lose a life.
The frog starts each level with three lives, shown as little hearts in the corner of the screen. Each time the frog is hit by a platform or an obstacle, they lose one life. Upon losing all lives, the frog will start over at the beginning of the level.



THE SCIENCE BEHIND THE HAPPY HOPPER
Happy Hopper is a brain game that requires the user to time their jumps in order to land safely on each platform and climb as high as possible. This exciting game helps stimulate the cognitive abilities related to Response Time, Estimation, and Inhibition.
Response Time

Response Time (also known as reaction time) refers to the amount of time that takes place between when we perceive something and when we respond to it. It is the ability to detect, process, and respond to stimuli.
Our ability to appropriately respond to stimuli in a timely and efficient manner depends on many factors. This includes our ability to perceive, process, and respond to the situation at hand.
- Perception: Seeing, hearing, or feeling a stimulus with certainty is essential to having good reaction time. And example is when someone shoots a racing pistol, the runners must react to the sound.
- Processing: In order to have good reaction time, it’s necessary to be focused and understand the information well. For exmpale, those same runners will know the difference between the pistol and the other background noises. It tells them it’s time to start running (process the stimulus).
- Response: Motor agility is necessary in order to be able to act and have good response time. When the runners perceives and correctly processes the signal, they start moving their legs (respond to the stimulus).
Estimation

Estimation is one of our most important neuropsychological functions, as many of our daily activities depend on our ability to estimate speed, distance, or time. Estimation could be thought of as the mental process that allows predicting an appropriate response based on incomplete knowledge.
Estimation allows us to predict an object’s future location based on its current speed, distance, and time. The brain processes the information from your eyes and determines what to do and how fast to do it.
We also use our estimation ability in perceptive thought processes. Once the brain has decided which information it’s going to process, it evaluates and estimates its distance, speed, etc. In order to accurately process the information you receive and make an estimation, you need to use past experiences as a reference. Using real-life previous situations will help ensure that you make an informed estimation about what might happen.
Inhibition

Inhibition is the ability to control impulsive or automatic responses and create measured responses by using attention and reasoning.
This cognitive ability is one of our Executive Functions and contributes to anticipation, planning, and goal setting. Inhibition, (also known as inhibitory control) blocks behaviors and stops inappropriate automatic reactions. This allows us to replace an undesired, automatic response for a better, more thought-out response that’s adapted to the situation.
Here are some examples…
- If you get bitten by a mosquito, it’s normal to want to scratch. People with good inhibitory control will be able to keep themselves from scratching the bug bite, even though it itches. Poor inhibitory control may make it difficult to resist scratching the itch, causing the bug bite to bleed and scab.
- Imagine you’re having dinner with your family and your brother-in-law (who you don’t like very much) says is being very annoying. You might have a hard time keeping yourself from calling him out or yelling at him. However, if you have good inhibitory control, you’ll be able to control yourself and keep calm. If you have poor inhibitory control, you risk ruining the dinner.
- It’s common to see office situations where employees are automatically doing distrating things. This includes looking at their phone, talking to colleagues, or thinking about non-work things. If an employee has good inhibitory control, they will be more efficient workers.
Are you ready to test your Response Time and stimulate your cognitive abilities?
We hope you enjoy this hoppy-fun cognitive stimulation brain game! Also, we would love to hear your thoughts on this or any of our other games on our special media platforms. And don’t forget to keep an eye out for more exciting brain games from CogniFit!