Feeling Tired After Socializing? Here’s What’s Happening in Your Brain
Many people notice a weird mismatch: a conversation can be friendly (even fun) and still feel draining. That’s not automatically a sign that something is “wrong” with you, or that you’re antisocial, or that you’re secretly an introvert in disguise. You can enjoy a conversation and still feel mentally wiped out afterward, and that contradiction is the key. Social interaction doesn’t just involve talking; it requires the brain to stay alert, responsive, and fast while processing multiple streams of information at once. Much of this mental work goes unnoticed during the interaction itself. It becomes visible only when the energy runs out – and social fatigue sets in.
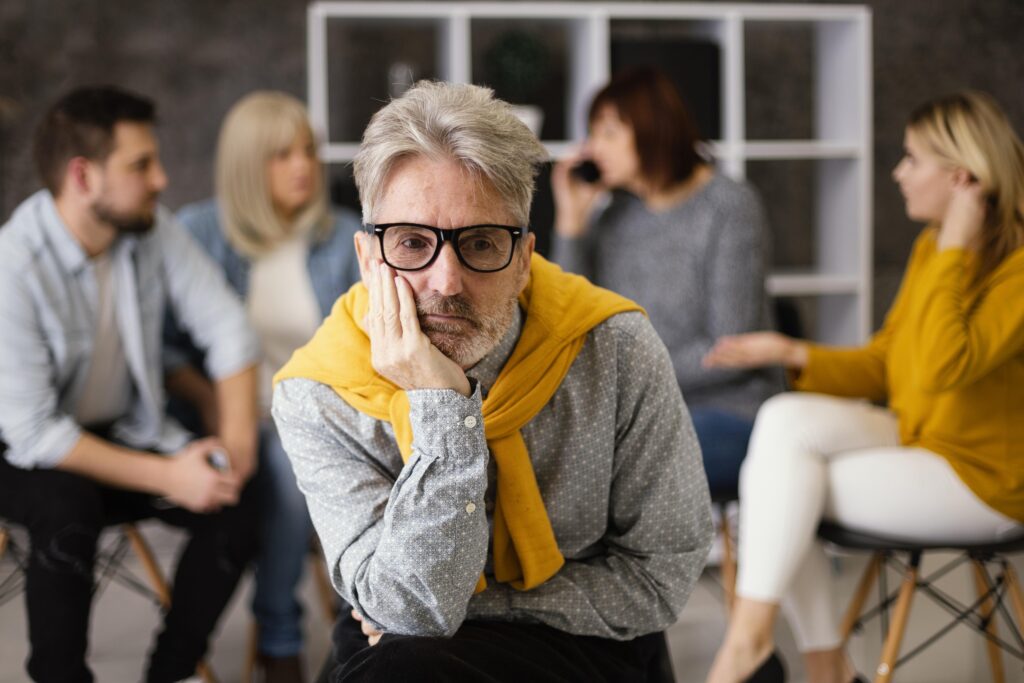

You leave a conversation that went well. There was no conflict, no awkward moment, nothing unpleasant. Yet a short time later, your mind feels heavy. Thinking slows down. Even small decisions start to feel effortful. This experience is surprisingly common. It shows up after meetings, family gatherings, long calls, group discussions, and even relaxed one-on-one conversations. Because it feels personal, it’s often explained in personal terms – as a lack of social energy or a mismatch in personality. But mental fatigue after social interaction is rarely about who you are. More often, it reflects how much sustained cognitive effort the interaction required.
Social interaction feels natural, but it is not mentally simple. Conversations move quickly, shift constantly, and demand continuous adjustment. Unlike many tasks, they rarely offer clear pauses where the brain can fully reset. To understand why socializing can be mentally exhausting – even when it’s enjoyable – it helps to look at what the brain is actually doing during everyday interaction.
Social Interaction Is a Cognitive Task, Not “Just Talking”
From the outside, conversation looks effortless. Words flow, responses come quickly, and most people don’t appear to be “thinking hard.” But that smoothness is deceptive. In everyday conversation, timing is tight. People often respond within fractions of a second. To do that, the brain cannot wait until the other person finishes speaking. It must begin preparing a response while still listening, interpreting meaning, predicting intent, and tracking social cues.
This creates constant overlap. Comprehension, response planning, language production, and social interpretation all run at the same time. The brain is juggling multiple processes continuously, without clear separation. Conversation, then, is not one task. It’s a coordinated system of tasks operating in real time. The effort is subtle, but persistent – and persistence is what leads to fatigue.
From a neuroscience perspective, this kind of parallel processing places continuous demands on networks involved in attention control, language processing, and executive function.
The Hidden Workload: Attention and Monitoring
During social interaction, attention rarely rests. You’re not only following words. You’re tracking tone, pauses, facial expressions, body language, and emotional shifts. You’re noticing whether someone seems engaged, confused, amused, or distracted.
At the same time, attention must filter information. Background noise, side conversations, internal thoughts, and environmental distractions all compete for processing space. Choosing what to focus on – and what to suppress – requires effort.
Working memory supports this process by holding relevant pieces of information in mind: what was just said, what still needs to be addressed, and what you want to say next. Because working memory capacity is limited, the more information it must juggle, the higher the cognitive demand becomes.
When these systems operate near their capacity for extended periods, mental fatigue becomes a predictable outcome rather than an exception.
Social interaction keeps this system running continuously. There is no true “idle mode.”
Working Memory Under Pressure: Following the Thread
Conversations are dynamic. Topics shift. Details accumulate. Emotional context adds another layer of information to manage. Working memory must update constantly while remaining ready to support quick responses.
Even listening can be demanding. Following a group discussion requires deciding who to attend to, when to shift focus, and how to integrate multiple viewpoints into a coherent understanding. When the environment is noisy or the conversation moves quickly, this demand increases further.
None of this means the brain is malfunctioning. It means it is working – and work consumes resources.
Self-Regulation: The Mental Cost of “Being Social”
A large portion of social effort happens internally. People regulate reactions, choose appropriate wording, manage tone, and decide when to speak or stay silent. They monitor how they come across and adjust behavior in real time.
This self-regulation supports smooth interaction, but it requires mental energy. Monitoring oneself, especially in situations where impressions matter, adds another layer of cognitive demand.
This type of self-regulation relies on executive control processes, which are known to be sensitive to sustained mental effort.
This effort is not about being artificial or inauthentic. It’s about coordinating behavior within shared social norms. The cost comes from sustained monitoring, not from insincerity.
Over time, this invisible effort can contribute significantly to mental exhaustion.
Why Enjoyment and Mental Fatigue Can Coexist
One of the most confusing aspects of social exhaustion is that it often follows positive experiences. Many people expect that if something was enjoyable, it shouldn’t be tiring. But enjoyment and cognitive effort are not opposites.
An engaging conversation often demands more attention, more responsiveness, and more emotional processing. The brain is highly active, not relaxed. That involvement can feel satisfying – and still be taxing.
This explains why someone can leave a meaningful conversation feeling emotionally enriched and mentally drained at the same time. The interaction worked – and the brain paid the cost.
Context Matters More Than Personality Labels
Social fatigue is often explained through personality traits, but context is frequently a stronger factor.
A quiet one-on-one conversation differs greatly from navigating a group discussion. A casual chat differs from a conversation where decisions, evaluations, or social roles are involved. Short interactions place very different demands on the brain than long, uninterrupted ones.
Even the same person can experience social interaction as energizing in one context and exhausting in another. This variability makes sense when social interaction is treated as a task with changing cognitive demands rather than a fixed test of personality.
The Accumulation Effect: Why Fatigue Appears Later
Social exhaustion rarely arrives suddenly. It builds. Because conversations don’t usually feel overwhelming in the moment, the brain keeps going. Attention remains engaged. Working memory stays active. Self-regulation continues quietly. There is no obvious signal to stop.
Cognitive fatigue often emerges after the task ends, when the brain no longer needs to maintain performance in real time.
Only afterward does the cost become visible: slower thinking, reduced motivation, difficulty focusing, or the desire to withdraw from further interaction. Understanding this accumulation effect helps explain why fatigue can feel delayed, and why it can be confusing when it finally appears.
Managing Cognitive Load in Everyday Social Life
The goal is not to avoid social interaction, but to make it cognitively sustainable. The following strategies focus on reducing unnecessary mental strain in everyday social situations.
1. Build in Mental Recovery
After demanding social interactions, shifting to lower-demand activities allows cognitive resources to recover. This might involve quiet time, routine tasks, or reduced stimulation rather than complete isolation.
2. Reduce Unnecessary Self-Monitoring
In some settings, especially virtual ones, constant self-focus increases cognitive effort. Minimizing unnecessary self-monitoring can lower mental load.
3. Simplify High-Demand Conversations
Reducing background noise, limiting multitasking, and keeping conversations focused helps decrease demands on attention and working memory.
4. Avoid Stacking Cognitive Demands
Combining intense social processing with complex decision-making or heavy multitasking can amplify fatigue. Separating these demands makes both more manageable.
5. Support Cognitive Flexibility and Mental Efficiency
Because attention and working memory are central to conversation, maintaining these cognitive abilities can help the brain handle demanding situations more efficiently. Activities that challenge memory, attention, and mental flexibility may support overall cognitive resilience, especially when combined with good recovery habits and realistic expectations.
This approach does not treat cognitive training as a quick fix, but as one of several ways to support the mental systems that social interaction relies on.
Conclusion
Mental exhaustion after social interaction becomes far less mysterious when conversation is understood as a cognitively demanding activity. It requires sustained attention, continuous updating of information, rapid response planning, and ongoing self-regulation.
Feeling tired afterward is not a personal failure. In many cases, it’s simply the result of doing complex mental work for an extended period of time.
Understanding this reframes social fatigue not as a flaw, but as a natural outcome of how the brain handles rich, demanding human interaction.
The information in this article is provided for informational purposes only and is not medical advice. For medical advice, please consult your doctor.