Childhood Dementia and Early Detection
childhood dementia
Childhood Dementia – A Complete Review
Some early warning signs to watch out for include memory loss, confusion, and problems with concentration, comprehension, learning or communication. Also be on the look out for personality changes.
Use a Test Doctors Trust – Childhood Dementia
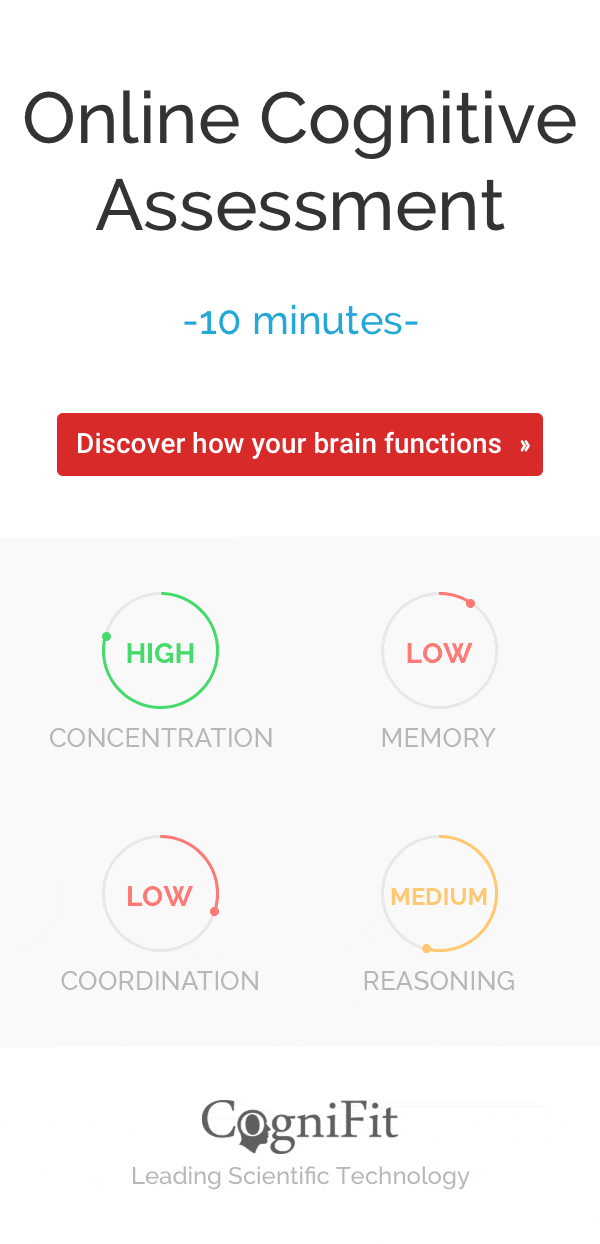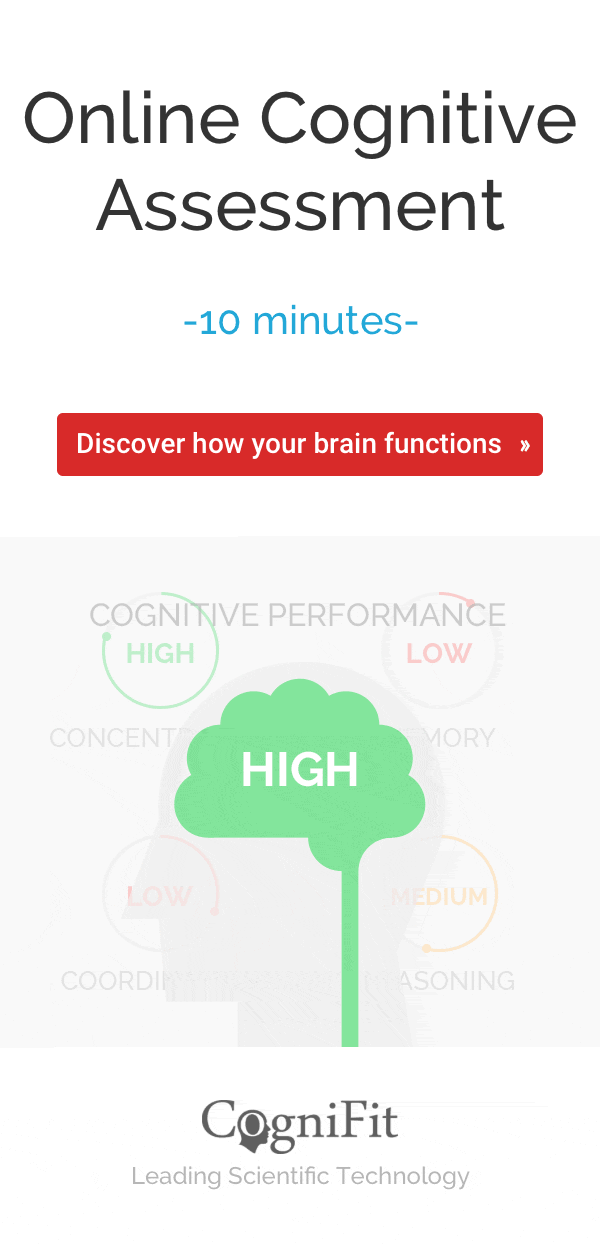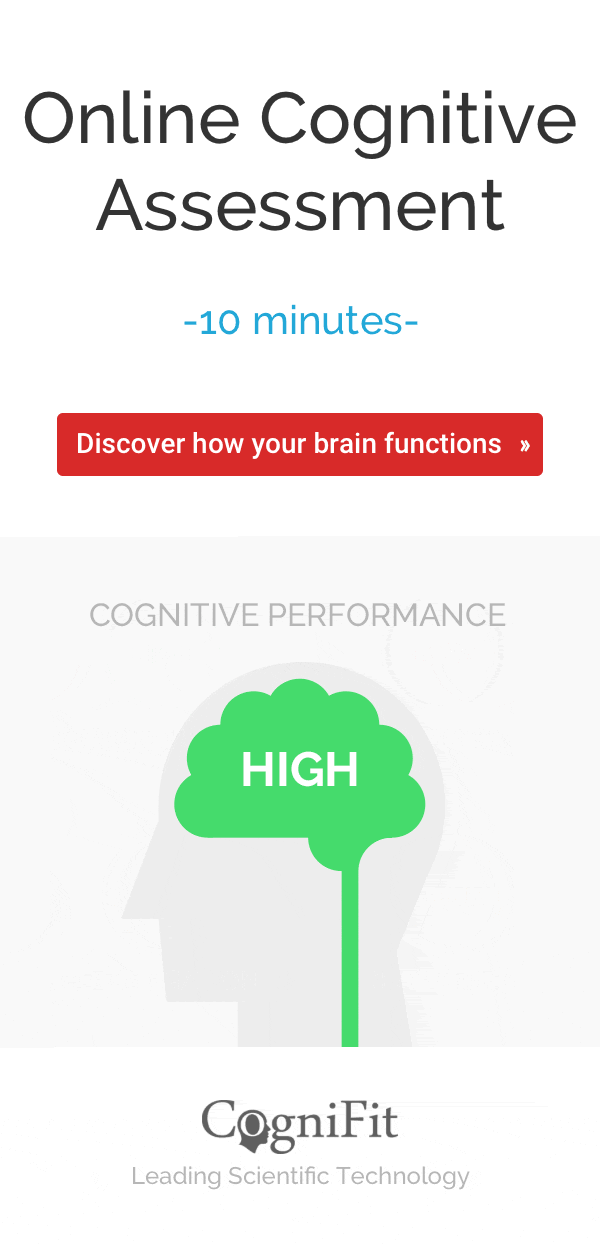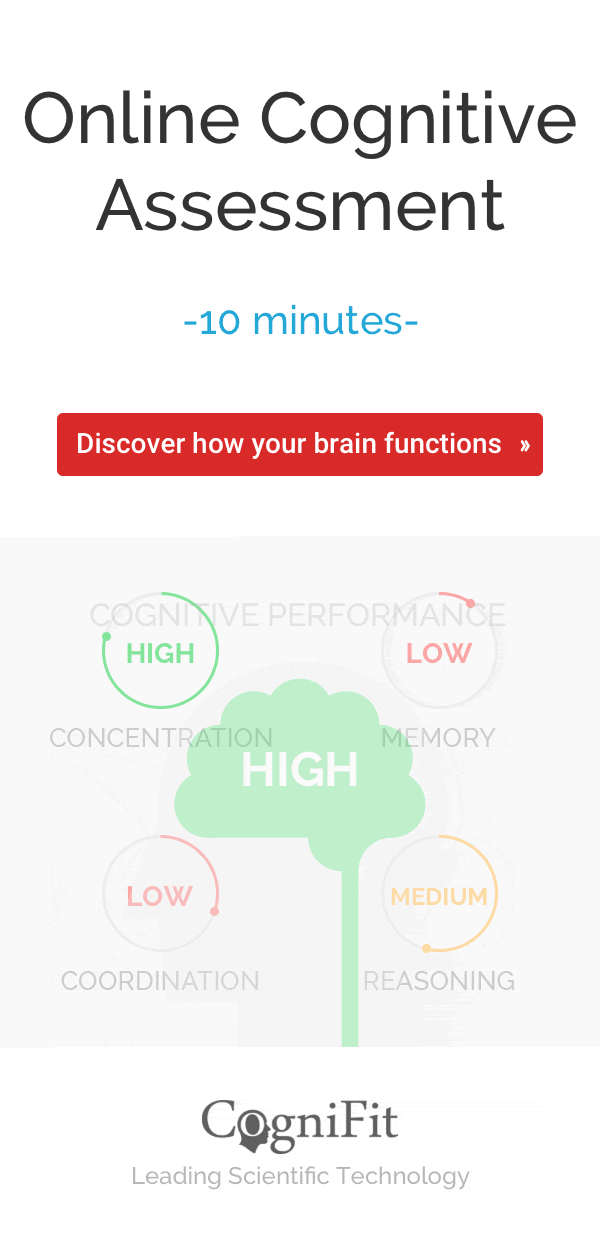
Take a quick memory test as a screen for childhood dementia, the MemTrax memory test is the most widely used cognitive test and shows statistical significance in early detection of dementia.

For a complete follow up use our Cognitive Assessment Battery. Begin watching you and your loved one’s cognitive function over time.
With our innovative brain training programs, you can get a personalized experience that stimulates the neurons inside your brain and helps keep your brain healthy.
Research has shown that our Brain Training Games can reverse cognitive decline and may help prevent Alzheimer’s disease and childhood dementia.
How long do children with childhood dementia live?
Childhood dementia facts and statistics. This does not include those born with common ailments such as cystic fibrosis. Every 11 minutes a child dies with Alzheimer’s disease. 42,000 people die annually. The average age of dementia is just 27 years old. According to the National Institute on Aging.
What is the youngest age to get dementia?

Dementias are not often diagnosed in young people and childhood dementia disorders are considered rare. Approximately 60% older people have dementia between 50 and 70 years or older. Typically, the term Young Aged dementia, Early Age dementia or Worklife Dementia is used when someone is diagnosed as having dementia at a younger age not childhood dementia.
Late infantile dementia and niemann pick type c diagnosis happen early in life and children progress quickly in childhood dementia. Research at the children’s hospital fight to stop the progressive brain damage and better understand the metabolism lysosomal disorders to prevent brain iron accumulation.
Life expectancy is grim for childhood dementia as adults struggle to produce more research for further investigation as they lack communicating personality. Seizures lose and hearing lose go hand in hand with inborn errors.
Does childhood dementia go away?
Childhood dementias are commonly known as neuronal ceroid lipofaccinosis. It is possible to find 14 different kinds of nlc disease. Currently none of these 14 illnesses has been treated.
Causes of Childhood Dementia
The most common cause of child dementia is neuro-ceroid lipofusecinosis, a grouping of disorders which cause lysosomal and gene expression. Globally the number of NCL deaths is a staggering 78% per 100,000 people and is one of the leading causes of childhood dementia.
NCLs are characterized by severe neurodegenerations in the brain and accumulation of lipofluorescent storage material in neurons. The classification for different types of NCL varies widely from a disease-causing gene to a disease-causing gene. Early diagnosis may help lead to a better treatment and increased life expectancy of this rare genetic disorder.
Other Lysosomal Storage Diseases Caused Childhood Dementia
In addition to NCLs, other lysome store disorders including the type A Niemann’s Pick disease’ and the mucolysaccharidose can cause childhood dementia.
NPP is another neurodegenerative disease that is found in young children – from childhood until the teens. Usually, a mutation in “NPC1″ or ” NPC-2 ” genes can cause the development of autoimmune diseases.
The disorder is the consequence of poor lipids and cholesterol synthesis and is characterized by the accumulation fatty acids in the brain, liver, spleen, and the lungs in childhood dementia. NPC causes dementia primarily symptomatic when schoolchildren are not aware.
Childhood Dementia Symptoms

To try to catch the disease onset as early as possible keep your eyes out for common dementia symptoms including: trouble interacting with other children, abnormal communicating personality, seizures, the child’s experience, abnormal accumulation of lifestyle errors. Maybe consider visiting a children’s hospital and view childhood dementia results.
They can analyze cell types and investigate the genetic component that plays a significant role for childhood dementia. AP0E4/4 Genetic testing information is a large contributor to dementia. More research continues to investigate symptoms of different groups to compare the childhood dementia results to adult forms that appear in different ages.
A child’s experience is traumatic and personality changes may occur as they suffer in life through disease onset. The specialist team can help establish a diagnosis of childhood dementia as neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses, peroxisomal disease neurodegeneration, or another rare genetic disorder.
Childhood Dementia Disorders

Progressive brain damage can cause hearing lose, brain iron accumulation, epileptic seizures, memory loss confusion trouble, hyperactivity emotional issues, progressive loss of motor skills, and loss of cognitive function at different ages. Further information is required for better understanding and effective treatments.
Clinical studies are ongoing for Kufs disease, metabolism lysosomal disorders, niemann pick type c, sanfilippo syndrome, neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses, and peroxisomal disease neurodegeneration.
Early infancy or late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis is caused by inborn errors and progress quickly for childhood dementia. Further investigation of young patients and genetic testing might help affected children and affected families better understand what they are dealing with.
A specialist team may be required to pinpoint which disease it could be with childhood dementia. Batten disease may be different in other children and the way they might suffer. Brain metabolism and retinal degeneration occurs in most children with these diseases.
Special aspects of palliative therapy in NCL
Several of these problems involve the palliative treatment for a person diagnosed with NCL disease. Recognition is difficult due to the difficulty of communicating later in a patient. The painful experience must be evaluated thoroughly by an expert.
In children abdominal pain may be caused by gastrointestinal hypertrophy or poor nutrition, but many other causes should be considered. Seizures lose, hyperactivity emotional issues in children might help us better understand childhood dementia.
Key points remain that early detection might be the best treatment against early death for children facing childhood dementia. Look for showing signs across different groups as most patients have similar dementia experience. The degradation of cognitive abilities are not always obvious in the development of young children.
Memory Loss Confusion Trouble
Dementia in child and young adults are more often attributed to neuronal ceroidlipofuscinoses (NCL), an uncommon group of lysosomal storage disorders that are linked via the accumulation of the intracellular storage materials. Clinical characteristics can vary and the age of an individual is between 18 and 29. Diagnosing NCLs is difficult because 14 nephtalysmal NCLs are identified, and high phenotypic variations are observed in children with childhood dementia.
The genetic spectrum of NCL diseases

There are 14 NCLs to date, 14 are described. In many cases the NCL gene isn’t identified in all known ncl gene, although they present typical NCL symptoms and characteristic cell storage material. Intracellular localization and functions of defective NCL proteins are different: Four NCL types can be caused through defects in the lysostomial enzymes (CLS2, CLS10 and CSN13), others through defects in transmembranary RNA. A mutation causing the development of NCL is a common symptom in childhood dementia.
The clinical spectrum of NCL diseases
In most NCL forms patients are initially healthy and develop normally. Symptoms include visual loss, epilepsy and motor impairment that progress slowly but inexorably. Age at diagnosis starts as early as the age of adulthood. The number of symptoms is different. In a young child first symptoms may include standstills in psychomotor activity or ineffable epilepsy. When children start showing symptoms they usually start out with visual problems and then develop dementia.
If you or a loved one is showing signs of childhood dementia talk to your doctor. CogniFit does not offer any medical advice. This blog is for entertainment and educational purposes only. Childhood cancer is much more common, but childhood dementia is also another terrible disease hurting people around the world.
Childhood Cancer – childhood dementia
Childhood cancer is a type of cancer that affects children. It can be treated, but it’s important to catch it early. There are many different kinds of childhood cancer, and they all need to be treated differently. Similar to childhood dementia, early diagnosis and treatment is the best chance a child has for beating cancer. A great free dementia care resource can be found on that link.